Keep Your Eyes On: A Prospective Device for Self-Monitoring Vision
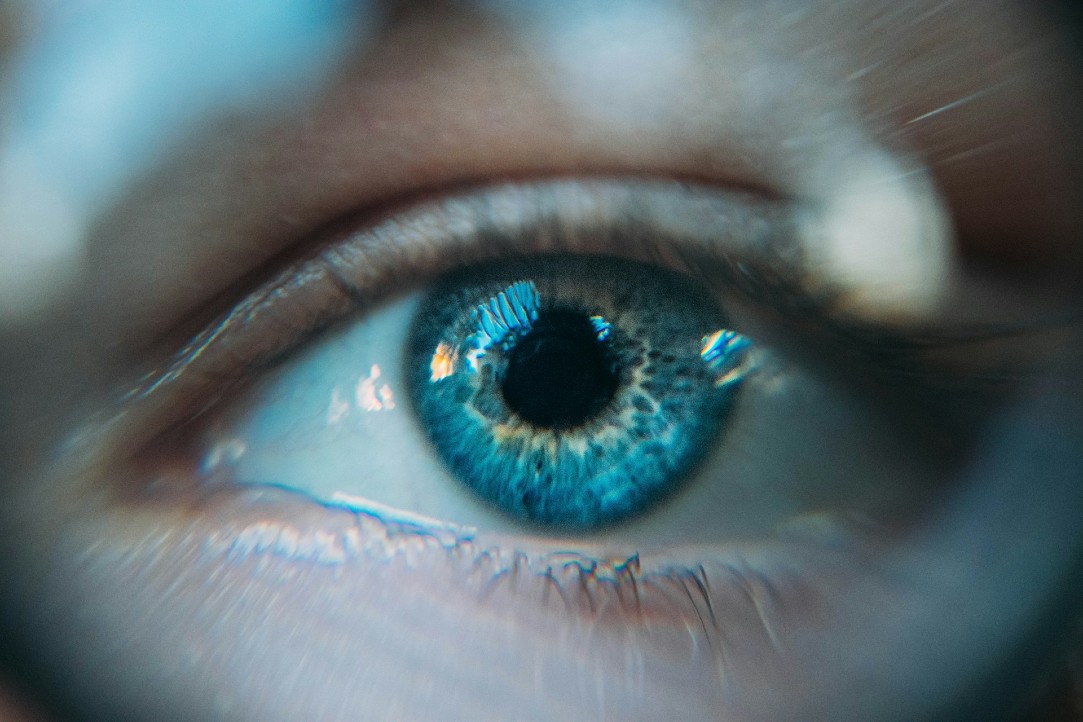

As part of the Strategic Project 'Success and Self-Sustainability of the Individual in a Changing World,' scientists at HSE University have conducted a study to develop an electronic device designed to reduce the risk of occurrence and progression of eye diseases.
In the digital age, the continuous use of gadgets and prolonged exposure to digital screens exacerbate health risks and are increasingly recognised as a public health problem. Statistics reveal that the number of hours spent in front of screens has increased dramatically over the past decade. Researchers worldwide attribute the increasing incidence of myopia in children and adolescents to this particular trend.
According to a survey conducted in Western Europe, only 50% of respondents regularly have their eyesight checked, while others tend to ignore early symptoms of visual impairment, which can eventually lead to serious vision problems, such as the progression of myopia in adolescents and hyperopia in adults. Using a personal device for self-monitoring vision can help prevent the progression of certain eye diseases: recent studies in Australia confirm that early detection of vision problems leads to better treatment outcomes and helps prevent the disease from worsening.
Pavel Korolev, in collaboration with a group of scientists, have begun developing a device for monitoring one's vision without the need to consult a healthcare provider. Their work is carried out in the framework of the Strategic Project 'Success and Self-Sustainability of the Individual in a Changing World.'
The researchers have published a report in which they analyse the structure of the human eye, vision parameters along with their normal values, monitoring methods, software and hardware for measuring eye parameters, as well as diseases, symptoms, and pathologies of the organ. As a result, the scientists have identified the primary requirements for a prospective device intended for independent vision monitoring.
The team working on the project is developing an electronic device capable of providing recommendations for eye rest and alerting the person to the need of consulting a healthcare provider if a visual impairment is detected. The goal is to help people mitigate the risks of developing eye diseases and prevent their progression. According to Pavel Korolev and the team, this can have a positive effect on overall human health by improving emotional well-being, interactions with the outside world and other people, safety at work and at home and productivity, and by slowing down the aging of the brain.
The scientists focus on the key parameters of human vision: intraocular pressure, field of vision, colour perception, visual acuity, visual evoked potentials, and eye refraction. Most existing devices for measuring these parameters are certified medical equipment, which is not always accessible for self-use and often necessitates professional assistance.
During the study, the scientists also determined that the critical flicker fusion frequency (cFFF) can be measured independently by an individual, while serving as an indicator of visual acuity. The cFFF refers to the frequency at which light flashes must occur for the human eye to perceive them as continuous light. This parameter can be used to assess the clarity and vividness with which a person perceives images in front of their eyes. Developing a self-monitoring device capable of measuring cFFF can mitigate the risk of undiagnosed glaucoma, cataracts, and other eye diseases.
Therefore, the development of a personal device for self-monitoring vision, aligning with the trend of digital medicine, can become a public health solution, offering potential benefits for promoting health and well-being in the digital age.
The prospective device will be particularly relevant for the at-risk group, including children, adolescents, and adults who spend prolonged periods working at a computer or handling small items. Furthermore, this technology can benefit individuals undergoing treatment or rehabilitation for optic nerve diseases, as it will help monitor the eye's ability to visualise and process information, enabling timely identification of complications or relapses. As an additional benefit, the device will not only assist patients but also alleviate the burden on healthcare providers.
See also:
Lost Signal: How Solar Activity Silenced Earth's Radiation
Researchers from HSE University and the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences analysed seven years of data from the ERG (Arase) satellite and, for the first time, provided a detailed description of a new type of radio emission from near-Earth space—the hectometric continuum, first discovered in 2017. The researchers found that this radiation appears a few hours after sunset and disappears one to three hours after sunrise. It was most frequently observed during the summer months and less often in spring and autumn. However, by mid-2022, when the Sun entered a phase of increased activity, the radiation had completely vanished—though the scientists believe the signal may reappear in the future. The study has been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics.
Banking Crises Drive Biodiversity Loss
Economists from HSE University, MGIMO University, and Bocconi University have found that financial crises have a significant negative impact on biodiversity and the environment. This relationship appears to be bi-directional: as global biodiversity declines, the likelihood of new crises increases. The study examines the status of populations encompassing thousands of species worldwide over the past 50 years. The article has been published in Economics Letters, an international journal.
Scientists Discover That the Brain Responds to Others’ Actions as if They Were Its Own
When we watch someone move their finger, our brain doesn’t remain passive. Research conducted by scientists from HSE University and Lausanne University Hospital shows that observing movement activates the motor cortex as if we were performing the action ourselves—while simultaneously ‘silencing’ unnecessary muscles. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.
HSE Seeks New Ideas for AI Agents: Initiative Competition Launched
HSE University is inviting researchers and lecturers to present concepts for new digital products based on artificial intelligence. The best projects will receive expert and technological support. Applications are open until December 19, 2025.
IDLab: Fascinating Research, Tough Deadlines, and Academic Drive
The International Laboratory of Intangible-driven Economy (IDLab) was established at the HSE campus in Perm 11 years ago. Its expertise in data processing and analysis allows researchers to combine fundamental studies with applied projects, including the development of risk and cybersecurity models for Sber. The head of the laboratory, Professor Petr Parshakov, and Senior Research Fellow Professor Mariya Molodchik spoke to the HSE News Service about IDLab’s work.
HSE Lecturers Awarded Yandex ML Prize 2025
The Yandex ML Prize is awarded to lecturers and heads of educational programmes who contribute to the development of artificial intelligence in Russia. This year, 10 laureates were selected from 300 applicants, including three members of the HSE Faculty of Computer Science (FCS). A special Hall of Fame award was also presented for contributions to the establishment of machine learning as an academic field. One of the recipients was Dmitry Vetrov, Research Professor at the HSE FCS.
HSE University and Banking and Finance Academy of Uzbekistan Sign Memorandum on Scientific Cooperation
The partnership aims to foster academic collaboration in the fields of global economics, sustainable development, and Islamic finance. Strengthening academic ties with Uzbekistan represents a promising direction for scientific exchanges and the implementation of international projects in sustainable development.
HSE Scientists Optimise Training of Generative Flow Networks
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science have optimised the training method for generative flow neural networks to handle unstructured tasks, which could make the search for new drugs more efficient. The results of their work were presented at ICLR 2025, one of the world’s leading conferences on machine learning. The paper is available at Arxiv.org.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.